Blog
Introduction
The first human species called Homo erectus lived in India around 2 million years ago.
Homo sapiens, the modern humans, were present about 70,000 years ago. They lived by hunting and gathering food.
What is Prehistoric?
A long time ago, there were no papers, no writing, and no books.
This time is called the Prehistoric period.
It was hard to know how people lived until scientists started digging and studying their tools, bones, shelters, and cave drawings.
People used paintings and drawings on cave walls to express themselves. This was the first type of art.
Periods of Prehistoric Times (based on tools used):
1. Palaeolithic Period (Old Stone Age): 2 million BC – 10,000 BC
2. Mesolithic Period (Middle Stone Age): 10,000 BC – 8000 BC
3. Neolithic Period (New Stone Age): 8000 BC – 4000 BC
4. Chalcolithic Period (Copper-Stone Age): 4000 BC – 1500 BC
5. Iron Age: 1500 BC – 200 BC
Stone Age in Quaternary Period:
Quaternary is divided into:
Pleistocene (20 lakh BC – 10,000 BC)
Holocene (10,000 BC – Present)
Pleistocene Age (Old Stone Age)
People used rough stone tools
They didn’t know farming
They lived by hunting animals
They stayed in rock shelters
Also known as the Ice Age or Old Stone Age
Found all over India except near rivers like Ganga, Yamuna, and Indus
Divided into 3 phases based on tools:
1. Lower Palaeolithic (up to 100,000 BC)
2. Middle Palaeolithic (100,000 BC – 40,000 BC)
3. Upper Palaeolithic (40,000 BC – 10,000 BC)
Lower Palaeolithic Age
People hunted and gathered food
They used tools like axes, choppers, and cleavers
Bori (Maharashtra) is the earliest site
Tools were made from limestone too
Types of Tools:
Chopper: Heavy stone tool with only one working side
Chopping Tool: Similar to chopper, but with two working edges
Hand Axe: More advanced than chopper, with narrow vertical edge
Cleaver: Like hand axe, but with flat horizontal edge
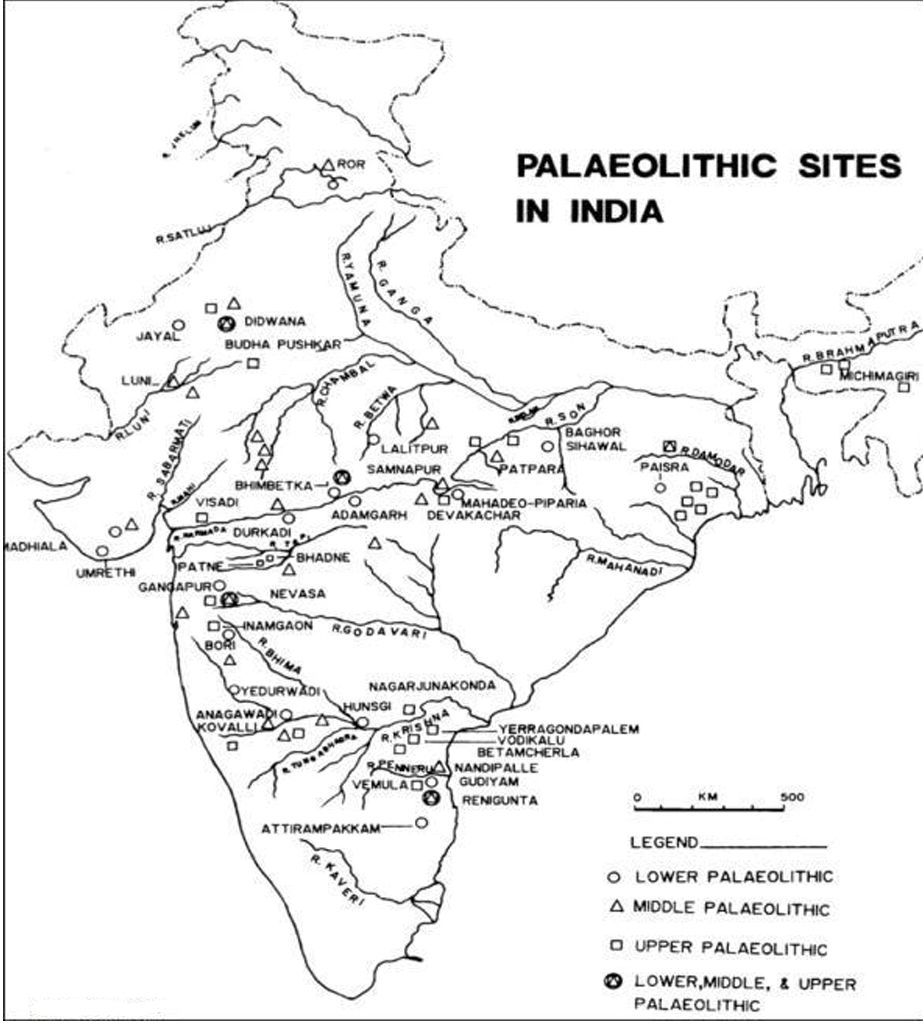
Important Sites:
Soan Valley (Pakistan), Thar Desert, Kashmir, Mewar Plains, Saurashtra, Gujarat, Central India, Deccan Plateau, Chotanagpur, North Cauvery, Belan Valley
Middle Palaeolithic Age
Tools were smaller, thinner, sharper
Made with flakes of stones
Types: Blades, Scrapers, Points
Sites: Belan Valley, Luni Valley, Narmada and Son Rivers, Bhimbetka (MP)
Upper Palaeolithic Age
Homo sapiens (modern humans) appeared
Tools were advanced blades, many made of bone
Found needle-like tools, burins, harpoons
Bhimbetka paintings belong to this age
Sites: Belan, Son, Chotanagpur, Orissa, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh
Mesolithic Age (10,000 – 8000 BC)
Weather became warm and dry
People moved to new areas
They used microliths (tiny stone tools)
Lived by hunting, fishing, and gathering food
Later, they domesticated animals
Dog was the first animal domesticated
Then sheep and goats were tamed
First humans settled in Ganga Plains
Rock paintings in Bhimbetka show birds, animals, and humans
Major Sites: Brahmagiri, Sojat, Bhimbetka, Godavari Basin, Vindhya, Narmada, Gujarat, UP
Tools: Blades, Triangles, Trapezes, Spears, Knives, Arrowheads, Sickles, Harpoons
Neolithic Age (8000 – 4000 BC)
People began farming and raising animals
Settled life started
They grew ragi, wheat, and horse gram
Discovered wheel and learned to make fire
Pottery appeared (black and grey types)
Houses made from mud
Burzahom (Kashmir): dogs buried with humans
Mehrgarh (Pakistan): early farming village
Important Sites: Burzahom, Gufkral (J&K), Mehrgarh, Chirand (Bihar), Daojali Hading (Tripura), Hallur (Karnataka), Paiyampalli (AP)
Tools: Heavy, polished tools; Celts used for digging
First use of copper
People knew crop rotation, irrigation, and harvesting
Lived in mud houses (round/rectangular) with mud stoves (chulha)
Pottery was black on red
Important Cultures:
Ahar/Banas (Rajasthan, MP): black & red pottery with white designs
Kayatha (MP): chocolate painted red ware
Malwa (MP/Maharashtra): buff pottery with red/black patterns
Jorwe (Maharashtra/MP): black-on-red with matte finish
Prabhas and Rangpur (Gujarat): shiny lustrous red ware from Harappan culture

Art in Prehistoric Times
Palaeolithic Art:
No painting found in Lower and Middle phases
Upper Palaeolithic had early art
Paintings: humans, animals, symbols, daily life
First rock paintings found in India (1867) by Archibold Carlleyle
Found in MP, UP, Telangana, AP, Karnataka, Bihar, Uttarakhand
Famous Sites: Bhimbetka, Lakhudiyar, Kupgallu, Jogimara
Black → Red → White colors in layers
Animals: long snouted creatures, lizards, fox
Humans shown as stick figures
Mesolithic Art
Most paintings come from this time
Themes: hunting, group dancing, animals chasing humans
Animals drawn naturally; humans drawn with bows, spears
Men, women, children shown – some nude, some clothed
Chalcolithic Art
Shows contact between cave people and farmers
Paintings included pottery, metal tools
Designs less lively than earlier ones
Common patterns: lattices, grids, cross-hatchings
OCP Culture (Ochre-Coloured Pottery)
Found in Upper Ganga region
Bright red pottery with black painting
Same time as Late Harappan period
Found in flood-affected areas
People used copper tools, grew rice, barley, gram
Similar shapes to Harappan pots
Saipai (Etah, UP): copper hoards found with OCP
Ganga-Yamuna doab shows close link between OCP and copper hoards
